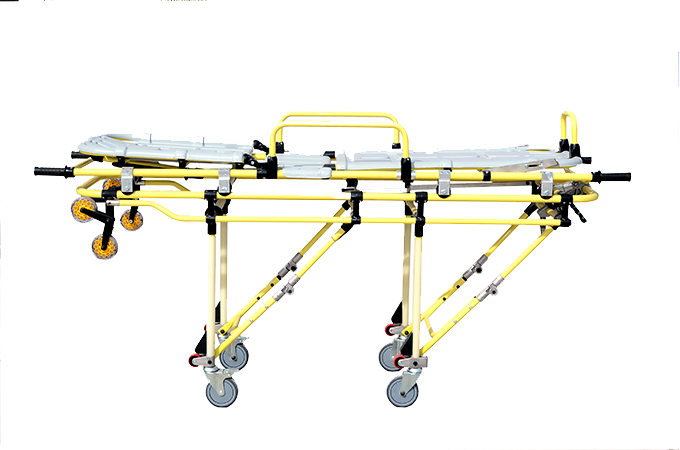
Transfer Stretcher
Transfer Stretcher
Transfer stretcher is essential pieces of medical equipment used to safely move patients between beds, between beds and gurneys, and between other flat surfaces. They provide a sturdy and stable platform to transfer individuals who have limited or no mobility.
Transfer stretchers date back to the early 20th century when they were first developed as an alternative to canvas stretchers. The earliest models were basic flat boards with handles on each side. Designs have evolved over the decades to incorporate features like side rails, brake systems, and hydraulic lifts. Materials have also advanced from wood to metals like aluminum and stainless steel.
Today, transfer stretchers are a standard fixture in hospitals, nursing homes, assisted living facilities, and emergency response settings. They help caregivers safely maneuver patients weighing up to 700 pounds depending on the model. When used properly, they reduce the risk of injury to both patients and healthcare staff. Their adjustable nature makes them adaptable across various healthcare environments and situations.
What is a Transfer Stretcher?
A transfer stretcher is a patient transport device used to safely move injured or mobility-impaired individuals between locations and surfaces. It consists of a lightweight frame made of aluminum or steel with a durable fabric stretcher bed attached.
Transfer stretchers allow caregivers to lift and transfer patients with limited mobility in a variety of settings, including hospitals, nursing facilities, and private residences. They provide a stable and comfortable platform for the patient while reducing the physical strain on caregivers maneuvering the patient.
Unlike traditional canvas stretchers that require two or more people to carry the patient, transfer stretchers are designed with glides or wheels that enable one person to move the occupied stretcher. The patient lies on the fabric bed surface while the caregiver pushes or pulls the stretcher frame along the floor or ground. This greatly improves transport efficiency and safety.
Some key features of transfer stretchers include folding frames for storage, 3-4 swivel casters for maneuverability, adjustable height settings, and padded bed sections for patient comfort. They are a versatile tool for patient handling personnel and can be used with patients of various sizes and mobility levels. Models with bariatric weight capacities are available for larger patients.
Overall, transfer stretchers allow for the safe and dignified movement of patients while promoting proper body mechanics for the caregiver. They are an essential component of a professional patient transfer and transport system.
Key Features
Transfer stretchers are designed to be highly portable and maneuverable for safe patient transfers. Here are some of the key features:
Lightweight
Transfer stretchers are constructed using lightweight metals like aluminum to minimize the overall weight. This allows caregivers to more easily lift, carry, and maneuver the stretcher without excessive strain. Lightweight stretchers typically weigh between 15-30 pounds. The reduced weight makes them ideal for frequent transfers and for use by a single caregiver.
Adjustable
The height of the stretcher can be adjusted to properly align with the surface the patient is being transferred from and to. This prevents caregivers from having to lift patients up or down more than a few inches during transfers, reducing risk of injury. The adjustable height also allows the stretcher to be positioned at a comfortable working height for the caregiver.
Easy to Maneuver
Transfer stretchers have steering handles at both ends to make maneuvering straightforward. Large wheel casters allow the stretcher to smoothly roll and change direction with little effort. The wheels have locks to keep the stretcher securely in place once positioned. The maneuverability enables safe and efficient movement even in tight spaces.
Materials
Transfer stretchers are made from durable, lightweight materials that allow for easy maneuverability while maintaining patient safety and comfort. The most common materials used are:
Aluminum – Stretcher frames are typically constructed from aluminum alloys which provide strength while remaining lightweight. Aircraft grade aluminum is often used for its high strength-to-weight ratio.
Nylon – Nylon webbing is used for the stretcher bed and patient restraints. Nylon is flexible, abrasion-resistant and able to withstand exposure to bodily fluids.
Fabrics – The bed surface is made from fabrics such as polyester, nylon, or cotton. These fabrics allow for airflow and drainage while providing comfort. Some models feature replaceable fabric covers that are machine washable. Antimicrobial fabrics help reduce the spread of germs.
Safety Considerations
When using a transfer stretcher, there are some important safety factors to consider:
Weight Limits
Adhere to the maximum weight limit specified by the manufacturer. Overloading the stretcher can cause damage and lead to dangerous collapse or tipping.
Check the weight capacity before transferring any patient. Make sure to account for the patient’s weight plus any additional equipment or items on the stretcher.
Do not exceed weight limits even if the stretcher seems to function normally when overloaded. The components may weaken over time.
Brakes
Always set the wheel locks when the stretcher is stationary. This prevents accidental rolling which could lead to injury.
Test that the wheel brakes are functioning properly before each use. Faulty brakes increase the risk of uncontrolled stretcher movement.
Engage both wheel locks for maximum stability when transferring a patient on or off the stretcher.
Restraints
Use the provided restraint straps to secure the patient. This prevents falling which could be catastrophic for some patients.
Make sure the restraints are tightened to be snug but not constricting. Monitor restraints regularly.
Position restraint straps carefully to avoid pressure sores or agitating injuries. Use extra padding if needed.
Only use restraints when necessary and remove them as soon as safely possible.
Maintenance
Proper maintenance of a transfer stretcher helps ensure it remains in good working condition. Here are some key maintenance tips:
Cleaning
Clean the stretcher after each use, especially if bodily fluids have contacted the surface. Use a disinfectant cleaner and follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
Pay close attention to cleaning the wheels, rails, and joints where dirt can accumulate.
Use a soft damp cloth to wipe down the vinyl or fabric surfaces. Avoid abrasive cleaners.
Check the manufacturer’s instructions to see if covers are removable and machine washable.
Disinfect and clean all accessories such as straps, pads, and belts.
Storage
Store the stretcher in a clean, dry area when not in use. Avoid exposure to moisture or extreme temperatures.
Ensure the stretcher is fully collapsed and secure during storage. Engage the wheel locks.
Charge the battery regularly if it’s an electric model. Don’t let it sit for long periods discharged.
Protect the stretcher from impacts, drops, or other damage during storage.
Parts Replacement
Inspect the stretcher before each use and replace any worn or damaged parts.
Wheels, cables, belts, joints, and locks are common parts needing replacement over time.
Only use manufacturer-approved replacement parts to ensure proper function and safety.
Follow all instructions for safe removal and installation of parts.
Perform routine lubrication of joints and cables.
Schedule preventative maintenance checks according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Common Models
There are a few major brands that produce quality transfer stretchers for medical facilities and emergency services.
Stryker
Stryker is one of the most well-known brands in stretchers and hospital beds. Their Power-PRO XT stretcher is designed for easy maneuverability and powered transport. It has an ergonomic, easy grip push handle and intuitive controls. The stretcher can support patients up to 700 lbs.
Ferno
Ferno makes the 35-EXL ProFlex stretcher which has a unique sliding chassis design to make loading and unloading patients safer and easier. The 35-EXL is built with an aluminum frame but has a softer feel due to FlexRide cushions. It can support patients up to 700 lbs.
Hill-Rom
The Hill-Rom P8000 stretcher has an easy to clean plastic frame and uses Linx central locking to ensure stability when moving patients. This stretcher has an easy lift mechanism to lower and raise the height for caregivers. It’s rated for patients up to 1000 lbs.
Stryker M1
The Stryker M1 is an inexpensive but reliable manual stretcher often used by EMTs for transporting patients. Despite the lower price point, it still offers good durability and can support patients up to 400 lbs. The M1 has integrated IV poles and fence-style rails.
Cost
Transfer stretchers can range widely in price from around $500 to over $2,000 depending on the model and features. Basic manual models tend to be the most affordable options. More advanced powered stretchers with electric controls and lift assist can cost $1,000 to $2,000. Prices are also impacted by the materials, with aluminum frames being more expensive than steel.
When deciding on budget, it’s important to consider your facility’s needs and frequency of use. If stretchers will be used often for many transfers per day, investing in a higher-quality and more ergonomic model can provide better durability and prevent staff injuries. For occasional needs, a basic stretcher may suffice. Maintenance costs may also be a factor, as higher-end models often require less frequent repairs and part replacements.
Overall, there are transfer stretcher options available at price points to suit different healthcare facilities and situations. Focusing on quality, ergonomics, and durability can provide better long-term value, especially for stretchers used regularly. Considering both upfront costs and ongoing maintenance expenses can help identify the most cost-effective solution.
Applications
Transfer stretchers have a number of important applications in the medical field. Some of the most common uses include:
Hospitals
Hospitals frequently utilize transfer stretchers to move patients between units and departments. Stretchers allow for safe and comfortable transport of patients that may have limited mobility or need to remain supine during transfers. Nurses and patient care techs rely on stretchers to transfer patients to diagnostic testing, the operating room, ICU wards, and more. Stretchers are an essential piece of hospital equipment and workflow.
Nursing Homes
Nursing homes and long-term care facilities require transfer stretchers to reposition and transport elderly or disabled residents. Residents often need assistance moving from their beds to wheelchairs, dining areas, therapy appointments, and other locations throughout the facility. Transfer stretchers with mobility features allow staff to safely maneuver residents. Stretchers help reduce risk of injury to both patients and caregivers.
Emergency Medical Services
Ambulances are equipped with specialized stretchers to safely secure and transport patients in emergency situations. EMTs and paramedics utilize ambulance stretchers to move patients from incident scenes into the vehicle and then into the hospital upon arrival. EMS stretchers have features like retractable wheels and rail systems to smoothly load the stretcher into the ambulance. Durability and ease of cleaning are important for EMS stretchers which see heavy use in unpredictable conditions.
Conclusion
Transfer stretchers are an essential tool for patient transport and mobility assistance. They allow caregivers to safely move patients between beds, procedure tables, imaging equipment, and more. Key features like height adjustability, removable stretchers, and locking wheel brakes enable safe patient handling for both the patient and caregiver.
While seemingly simple devices, transfer stretchers require care and maintenance to keep them functioning properly. This includes inspecting the brakes, wheels, and stretcher for any damage after each use. The materials used such as aluminum, nylon, and vinyl must also be kept clean.
There are many reputable models on the market from brands like Stryker and Ferno. Prices range from a few hundred to a couple thousand dollars depending on the features. Overall, transfer stretchers are indispensable for providing quality patient care and maintaining safety. With proper use and care, they can serve healthcare facilities for many years.